Morphine consumption is not modified in patients with severe pain and classified by the DN4 score as neuropathic☆
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Rouen university hospital, 1 rue de Germont, 76031 Rouen cedex, France
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Service d'Accueil des Urgences, Hôpital Charles Nicolle, 1 rue de Germont, 76031 Rouen, France.

Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Rouen university hospital, 1 rue de Germont, 76031 Rouen cedex, France
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Service d'Accueil des Urgences, Hôpital Charles Nicolle, 1 rue de Germont, 76031 Rouen, France.
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine and Surgery, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
- Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Centre hospitalo-universitaire Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, 75013 Paris, France
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
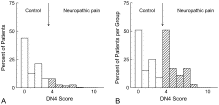
Fig. 1
Distribution of the DN4 score in the control (n=204) and neuropathic pain groups (n=35) in the studied population (A) and in each group (B). A DN4 score 4 or more defined the neuropathic pain.
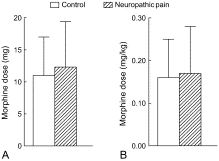
Fig. 2
Comparison of the morphine dose expressed as milligrams (A) or milligram per body weight (B) between the control (n=204) and neuropathic pain groups (n=35). Data are mean+SD. No difference was significant.

Fig. 3
DN4 questionnaire (English version), according to Bouhassira et al [35] .
Abstract
Neuropathic pain has been poorly investigated in the emergency department, although it is known to be less sensitive to opioids than other forms of pain. We tested the hypothesis that morphine requirements are increased in patients having severe pain classified as neuropathic using the DN4 score. We included adult patients with acute severe pain (visual analog scale ≥70), assessed using the DN4 score, and treated with intravenous morphine titration (bolus of 2 or 3 mg [body weight >60 kg] with 5-minute intervals between each bolus). Pain relief was defined as a visual analog scale 30 or less. Patients were divided into 2 groups: control group (DN4 score <4) and neuropathic pain group (DN4 score ≥4). The main outcome was the total dose of morphine administered. Data are mean±SD or median (interquartile range). Among the 239 patients included (mean age, 43+14 years), 35 patients (15%) had a DN4 score 4 or more. The main characteristics of the 2 groups were comparable. There were no significant differences between the 2 groups in morphine dose (0.16+0.09 vs 0.17+0.11 mg/kg, P=.32), number of boluses administered (3.5 [3-5] vs 3 [3-6], P=.97), proportion of patients with pain relief (75 vs 83%, P=.39), or morphine-related adverse effects (11% vs 3%, P=.14). In conclusion, morphine consumption was not significantly modified in patients having severe pain classified as neuropathic using the DN4 score as compared with a control group, suggesting that specific detection of neuropathic pain may not be useful in the emergency department.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Funding and support: The study was supported only by institutional sources.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


