Emergency diagnosis of Fournier's gangrene with bedside ultrasound
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
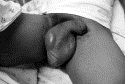
Fig. 1
The patient's swollen scrotum is shown.
Fig. 2
A focal collection (arrows) of gas is seen in the scrotum.
Fig. 3
A plain x-ray of the pelvis and scrotum showing scrotal gas (arrows).
Fig. 4
Two loops of bowel (arrows) are seen in the scrotum with occasional specs of bowel gas.
Abstract
Fournier gangrene is a life-threatening infection of the scrotal skin. Although originally thought to be an idiopathic process, Fournier gangrene has been shown to have a predilection for patients with diabetes as well as chronic alcohol abuse; however, it can also affect patients with nonobvious immune compromise. Because of potential complications, it is important to diagnose the disease process as early as possible. Ultrasound has been previously described to aid in the diagnosis of Fournier's gangrene. In patients with low to moderate suspicion of Fournier gangrene, it may provide a rapid and reliable diagnosis and differentiate the pathological process from mimicking entities such as scrotal edema or cellulitis. We present 6 cases of Fournier's gangrene diagnosed in the ED at the patient's bedside using ultrasound. None of the patients had a history of diabetes, and 5 had sources of infection determined.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..



