Predictive value of C-reactive protein at different cutoff levels in acute appendicitis
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
- Institute of Medical Research, Chang Jung Christian University, Changhua 500, Taiwan
Affiliations
- Department of Pediatrics, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
- Institute of Medical Research, Chang Jung Christian University, Changhua 500, Taiwan
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Children's Hospital, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan.

Affiliations
- Department of Pediatrics, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
- Institute of Medical Research, Chang Jung Christian University, Changhua 500, Taiwan
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Children's Hospital, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan.
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
Affiliations
- Evidence Base Medicine Center, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
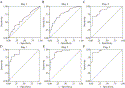
Fig. 1
Receiver operating characteristic curves for CRP in distinguishing between patients with appendicitis (both nonperforated and perforated) and patients with normal appendices (A-C), and between patients with perforated appendicitis and patients with normal appendices (D-F).
Abstract
Determining the different cutoff values of C-reactive protein (CRP) on the basis of how long the patient's symptoms were present can be used to early predict acute appendicitis. We analyzed retrospectively from 2001 to 2004 the hospital records of 568 patients who underwent appendectomies for suspected appendicitis. Receiver operating characteristic analysis has shown that CRP measurement can increase the diagnostic accuracy in acute appendicitis. The cutoff values of CRP concentration taken as the first, second, and third days after onset of symptoms that distinguish acute appendicitis from other acute abdominal diseases were 1.5, 4.0, and 10.5 mg/dL, respectively; the values that distinguish perforated appendicitis from other acute abdominal diseases were 3.3 mg/dL (first day), 8.5 mg/dL (second day), and 12.0 mg/dL (third day). The different cutoff values of CRP concentration may serve as a useful predictive parameter in the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis on the first 3 days after the onset of symptoms.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


