Comparison of available gum-elastic bougies
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. University of New Mexico MSC10 5560, 1 University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA. Tel.: +1 505 272 5062; fax: +1 505 272 6503.

Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. University of New Mexico MSC10 5560, 1 University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA. Tel.: +1 505 272 5062; fax: +1 505 272 6503.
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Medicine, Division of Critical Care, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001, USA
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
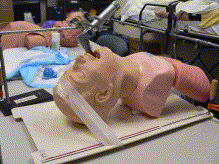
Fig. 1
Simulated difficult airway model.
Fig. 2
Simulated limited view of glottic opening.
Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to compare 4 different gum-elastic bougies (GEBs) for differences in success rate, speed of intubation, and device preference.
Methods
This was a randomized study of 4 different GEBs (Sunmed, Portex, Greenfield, and Eschmann) used by emergency medicine (EM) and anesthesiology residents and attending physicians on a simulated difficult airway model. Success, time to intubation, and personal preference were recorded for each participant. Data were compared with analysis of variance, χ2 and t tests, and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) where appropriate. P < .05 was considered significant.
Results
Twenty-one participants from EM (16 residents, 5 faculty) and 13 from anesthesia (9 residents, 4 faculty) were entered into the study. Overall success rates were 88% for Sunmed, 68% for Portex, 88% for Greenfield, and 79% for Eschmann. Participants were significantly more likely to be successful when using either the Sunmed or the Greenfield GEB compared with the Portex GEB (relative risk [RR] = 1.3, 95% CI = 1.0-15.6). Success rate by specialty was significantly different with 60 (71%) of 84 for EM physicians and 50 (96%) of 52 for anesthesiologists. Speed of intubation was a mean ± SD of 22.5 ± 9.7 seconds, with no significant difference by GEB or specialty. Participants were significantly more likely to prefer the Sunmed over the Greenfield (P = .001, RR = 6.9, 95% CI = 1.5-24.8) and the Eschmann over the Greenfield (P = .003, RR = 6.1, 95% CI = 1.6-63.0).
Conclusion
Emergency medicine physicians had better success rates using the Sunmed and Greenfield GEBs but low preference for the Greenfield GEB.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


