Elevated serum S100B protein and neuron-specific enolase levels in carbon monoxide poisoning
Affiliations
- Faculty of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine, Ondokuz Mayis University, 55139 Samsun, Turkey
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Tel.: +90 362 3121919/extention; fax: +90 362 4576041.

Affiliations
- Faculty of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine, Ondokuz Mayis University, 55139 Samsun, Turkey
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Tel.: +90 362 3121919/extention; fax: +90 362 4576041.
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Atatürk Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Internal Medicine, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Atatürk Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
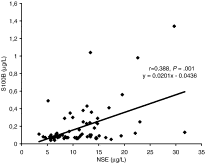
Fig. 1
The relation between serum S100B and NSE concentrations.
Fig. 2
S100B concentration in controls and patients, classified as unconscious and conscious. Median values are shown.
Fig. 3
Neuron-specific enolase concentration in controls and patients, classified as unconscious and conscious. Median values are shown.
Abstract
Objective
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning causes cerebral and generalized hypoxia. This study aimed to assess the possible use of serum glial marker S100B protein and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) as biochemical markers of hypoxic brain damage in acute CO poisoning.
Methods
Patients with acute CO poisoning admitted to the ED of 2 training hospitals (Ankara, Turkey) were included in this cross-sectional study. Serum levels of S100B and NSE were measured on admission. The patients were divided into 2 groups (unconscious and conscious). Twenty healthy adults were included in the study to serve as controls.
Results
A total of 70 patients poisoned by CO (mean age ± SD, 36.6 ± 16.3 years; 64.3% women) were enrolled. Although S100B concentrations were higher in patients than in the control group (P = .018), no significant difference was determined between patient and control groups with respect to NSE concentrations (P = .801). A positive correlation was noted between levels of S100B and NSE (r = 0.388; P = .001). The S100B and NSE values were higher in unconscious patients than in the control group (P = .002 and P = .013, respectively). Furthermore, S100B and NSE values were higher in unconscious vs unconscious patients (P = .047 and P = .005, respectively).
Conclusion
Elevated serum S100B and NSE levels were associated with loss of consciousness in CO poisoning in this series of patients. Serum S100B and NSE may be useful markers in the assessment of clinical status in CO poisoning.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


