Termination of drug-induced torsades de pointes with overdrive pacing
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Division of Medical Toxicology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, PO Box 800774, Charlottesville, VA 22908-0774, USA. Fax: +1 434 971 8657.

Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Division of Medical Toxicology, University of Virginia School of Medicine, PO Box 800774, Charlottesville, VA 22908-0774, USA. Fax: +1 434 971 8657.
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
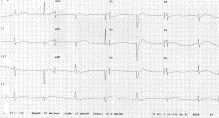
Fig. 1
Case 1 presenting ECG demonstrating sinus bradycardia with a QTc of 558 milliseconds.
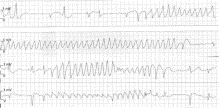
Fig. 2
Case 1 rhythm strips demonstrating TdP.

Fig. 3
Case 1 rhythm strips demonstrating a transvenous paced rhythm at a rate of 100 bpm.
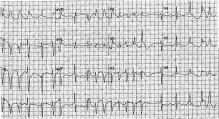
Fig. 4
Case 2 ECG on day 2 demonstrating a QTc of 647 milliseconds with short runs of polymorphic VT.

Fig. 5
Case 2 rhythm strip demonstrating a run of TdP.

Fig. 6
Case 3 presenting ECG demonstrating sinus bradycardia with a QTc of 528 milliseconds and a QRS of 108 milliseconds.
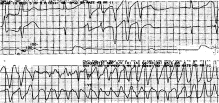
Fig. 7
Case 3 rhythm strip demonstrating TdP.
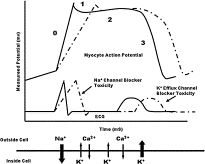
Fig. 8
Myocardial action potential with relationship to ECG and ion channel opening.
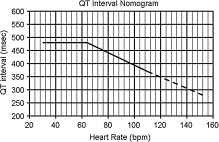
Fig. 9
QT interval nomogram. Adapted from Chan et al [9] .
Abstract
Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval is frequently encountered after medication overdose. Such toxicity can result in degeneration to torsades de pointes (TdP) and require overdrive pacing. We present 3 cases in which intentional medication overdose resulted in QTc prolongation with subsequent degeneration to TdP. Despite appropriate care, including magnesium therapy, each case required overdrive pacing for resolution of TdP. Although rarely encountered, patients with drug-induced TdP can be successfully managed with overdrive pacing.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


