Intranasal sufentanil for the treatment of acute pain in a winter resort clinic☆
ACEP Scientific Assembly, October 15, 2011
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. University of Utah, Division of Emergency Medicine, 30 North 1900 East, Room 1C026, Salt Lake City, UT 84132.

Correspondence
- Corresponding author. University of Utah, Division of Emergency Medicine, 30 North 1900 East, Room 1C026, Salt Lake City, UT 84132.
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
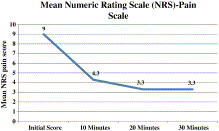
Fig.
Mean numeric rating scale—pain scale.
Abstract
Introduction
Painful extremity injuries are common patient complaints in resort clinics, urgent care clinics, and emergency departments. We hypothesized that intranasal (IN) sufentanil could provide rapid, noninvasive, effective pain relief to patients presenting with acute extremity injuries.
Methods
This was an unblinded, nonrandomized, observational study that enrolled a convenience sample of patients presenting to a university-affiliated ski clinic with acute moderate to severe pain associated with a traumatic injury between the months of January and March 2011. Patients were excluded if they reported an allergy to sufentanil or had hypoxia, significant head injury, or hypotension. Nurses administered IN sufentanil using an IN atomizer device. The nurse recorded patient-reported pain scores (0-10 scale) on arrival and at 10, 20, and 30 minutes after administration of sufentanil.
Results
During the study period, 40 patients were enrolled; 75% were men. The average age was 32 years (range, 16-60 years). The average dose of sufentanil was 37.7 μg. Five patients (12.5%) were given additional IN analgesia. Average pain on arrival was 9 (on a 10-point scale), and the mean reduction in pain scores was 4.7 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.67-5.57) at 10 minutes, 5.79 (95% CI, 4.81-6.77) at 20 minutes, and 5.74 (95% CI, 4.72-6.76) at 30 minutes.
Conclusion
In this limited observational trial, IN sufentanil provided rapid, safe, and noninvasive pain relief to patients presenting with acute traumatic extremity injuries. Given the ease of administration, this may serve as a viable option for use in other settings, such as urgent care clinics and emergency departments.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Study support: There was no source of support, including grant support for this study.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


