Predicting 7-day and 3-month functional outcomes after an ED visit for acute nontraumatic low back pain
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Emergency Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY 10467, USA. Tel.: +1 718 920 6626.

Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Emergency Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY 10467, USA. Tel.: +1 718 920 6626.
Affiliations
- Medical College, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
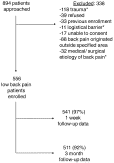
Figure.
Study flow diagram. *Patients were excluded for any trauma within the previous month, including motor vehicle collisions, falls, and direct blunt trauma to the back. Logistical barriers included patients who spoke a language other than English or Spanish or unavailability of research personnel. Medical and surgical etiologies of back pain included urinary tract infections, gynecologic pathology, sickle cell disease, and viral illness.
Abstract
Background
Recent work has shown that two-thirds of patients report functional disability 1 week after an emergency department (ED) visit for nontraumatic musculoskeletal low back pain (LBP). Nearly half of these patients report functional disability 3 months later. Identifying high-risk predictors of functional disability at each of these 2 time points will allow emergency clinicians to provide individual patients with an evidence-based understanding of their risk of protracted symptoms.
Object
The aim of the present study was to determine whether 5 high-risk features previously identified in various primary care settings predict poor functional outcomes among patients in the ED. The hypothesized predictors are as follows: LBP-related functional disability at baseline, radicular signs, depression, a work-related injury, or a history of chronic or recurrent LBP before the index episode.
Methods
We conducted a prospective observational cohort study of patients in the ED with a chief complaint of nontraumatic LBP, which the ED attending physician classified as musculoskeletal. We interviewed patients in the ED before discharge and performed a baseline assessment of functional disability using the 24-item Roland-Morris questionnaire. We also trichotomized the patient's baseline history of LBP into chronic (defined as 30 straight days with continuous LBP or a history of acute exacerbations more frequently than once per week); episodic (acute exacerbations more frequently than once per year but less frequently than once per week), or rarely/never (less frequently than once per year or no history of LBP). We performed telephone follow-up 1 week and 3 months after ED discharge using a scripted closed-question data collection instrument. The primary outcome was any functional limitation attributable to LBP at 1 week and 3 months, defined as a score greater than zero on the Roland-Morris questionnaire. We used logistic regression, adjusted for age, sex, and educational level, to assess the independent association between functional disability and each of the 5 hypothesized predictors listed above.
Results
We approached 894 patients for participation and included 556. We obtained follow-up on 97% and 92% of our sample at 1 week and 3 months, respectively. Two of the 5 hypothesized variables predicted functional disability at both time points: higher baseline Roland-Morris score (odds ratio [OR], 4.3; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.6-6.9) and chronic LBP (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.1-4.8) were associated with 7-day functional disability. These same 2 variables predicted functional disability 3 months after ED discharge—higher baseline Roland-Morris score (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-3.9) and chronic LBP (OR, 2.8; 95% CI, 1.5-5.2). The remaining 3 hypothesized predictors (depression, radicular signs, and on-the-job injury) did not predict functional outcome at either time point.
Conclusions
Patients in the ED with worse baseline functional impairment and a history of chronic LBP are 2 to 4 times most likely to have poor short- and longer-term outcomes.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


