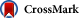Emergency neurosurgical care in patients treated with apixaban: report of 2 cases☆
Christopher Beynon

,x
, MDChristopher Beynon
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Neurosurgery, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany. Tel.: +49 6221 5636173.

x
Christopher Beynon
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Neurosurgery, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany. Tel.: +49 6221 5636173.
Anna Potzy, MD
, Andreas W. Unterberg, MD, PhD
, Oliver W. Sakowitz, MD, PhD
Department of Neurosurgery, Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany
 Article Info
Article Info
Publication History
Published Online: December 18, 2014Accepted: December 10, 2014; Received: November 26, 2014;
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
Figure
Computed tomography scans of patient 1 (on admission: A, after surgery: B) and patient 2 (on admission: C, after surgery: D).
A debate has emerged regarding the safety profile of direct anticoagulants, which are increasingly prescribed for the prevention of thromboembolic events. Despite favorable safety data derived from controlled clinical trials, the absence of specific antidotes for the management of hemorrhagic complications represents a major challenge for emergency physicians. Here, we present the first report on patients treated with the direct factor Xa inhibitor apixaban and conditions requiring urgent neurosurgical intervention (intracerebral hemorrhage, n = 1; subdural hematoma, n = 1).
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Sources of support: None.
© 2014 Elsevier Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Access this article on
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..