Paid sick leave is associated with fewer ED visits among US private sector working adults
Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
- Methodist Le Bonheur Center for Healthcare Economics, Fogelman College of Business and Economics, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152. Tel.: +1 901 678 3740.

Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
- Methodist Le Bonheur Center for Healthcare Economics, Fogelman College of Business and Economics, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152. Tel.: +1 901 678 3740.
Affiliations
- Department of Health Services Research, Administration and Policy, College of Public Health, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE 68198
Affiliations
- Department of Medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611
- Illinois Hospital Associations, Warrenville Rd, Naperville, IL 60563
Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
Affiliations
- Department of Surgery, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE 68198
Affiliations
- Division of Health Systems Management and Policy, School of Public Health, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
- Methodist Le Bonheur Center for Healthcare Economics, Fogelman College of Business and Economics, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
Figure
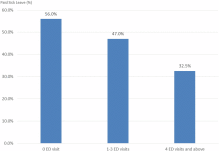
Percentage of respondents with paid sick leave by frequency of ED visit, US, NHIS (2012-2014).
Abstract
Context
The United States (US) is the only developed country that does not guarantee short-term or longer-term paid sick leave.
Objective
This study used a multiyear nationally representative database to examine the association between availability of paid sick leave and frequency of emergency department (ED) use among US private sector employees.
Study sample
We used the National Health Interview Survey data (2012-2014). The final study sample consists of 42,460 US adults between 18 and 64 years of age and working in nongovernmental private sector.
Results
Our results suggest that availability of paid sick leave is significantly associated with lower likelihood of ED use, for both moderate (1-3 times/year) and repeated users (4 or more times/year). After controlling for confounding factors, respondents with paid sick leave are 14% less likely to be moderate ED users (adjusted odds ratio, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.79-0.93) and 32% less likely to be repeated ED users (adjusted odds ratio, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.50-0.91).
Discussion
Although expansion of health insurance coverage under the Affordable Care Act has not been shown to reduce utilization of high cost health care services such as the ED, our study suggests other factors such as the availability of paid sick leave may do so, by allowing patients to seek care through other more cost-effective mechanisms (eg, primary care providers). To reduce ED utilization, health policymakers should consider alternative reforms including paid sick leave.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..