The development and experimental application of a new thoracostomy trocar
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, 153 Gyeongchun-ro (st), Guri-si, GyeongGi-do 471-701, Republic of Korea. Tel.: +82 31 560 2056; fax: +82 31 560 2059.

Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, 153 Gyeongchun-ro (st), Guri-si, GyeongGi-do 471-701, Republic of Korea. Tel.: +82 31 560 2056; fax: +82 31 560 2059.
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
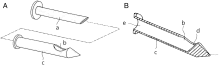
Fig. 1
The structure of the new trocar.
A, The mold and the stylet. B, A sectional drawing of the mold.
a, Stylet. b, Side hole. c, Mold. d, Inclined plane. e, Passageway for the chest tube.
Fig. 2
A diagram of chest tube insertion with the new trocar.
A, The penetration of the thoracic wall with the combined mold and stylet. B, The insertion of the chest tube after the removal of the stylet.
a, Thoracic cavity. b, Mold. c, Thoracic wall. d, Side hole closed by the stylet. e, Stylet. f, Chest tube.
Fig. 3
The 4 steps of chest tube insertion into a cadaver using the new trocar.
A, The creation of an incision in the skin with a surgical scalpel. B, The puncturing of the thoracic wall with the trocar, which is then pushed into the thoracic cavity. C, The drawing of the stylet out of the mold and the insertion of the chest tube through the mold. D, The removal of the mold from the thoracic wall.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..