Optimal Dosing of IV Ketamine for Procedural Sedation in Children in the Emergency Department - A Randomized Controlled Trial
Affiliations
- Wayne State University School of Medicine, Carman and Ann Adams Department of Pediatrics, Division of Emergency Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Michigan, 3901, Beaubien Blvd, Detroit, MI, 48201
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Wayne State University School of Medicine, Carman and Ann Adams Department of Pediatrics, Division of Emergency Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Michigan, 3901, Beaubien Blvd, Detroit, MI, 48201. Tel.: +1 313 745 5260.

Affiliations
- Wayne State University School of Medicine, Carman and Ann Adams Department of Pediatrics, Division of Emergency Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Michigan, 3901, Beaubien Blvd, Detroit, MI, 48201
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Wayne State University School of Medicine, Carman and Ann Adams Department of Pediatrics, Division of Emergency Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Michigan, 3901, Beaubien Blvd, Detroit, MI, 48201. Tel.: +1 313 745 5260.
Affiliations
- Wayne State University School of Medicine Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, 515 N. State Street, Suite 2000, Chicago, IL, 60654
Affiliations
- Department of Pharmacy Services, Children's Hospital of Michigan, 3901 Beaubien Blvd, Detroit, MI, 48201
Affiliations
- Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, 48201
Affiliations
- Department of Pediatrics, Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, 48201
Affiliations
- University of Minnesota Medical School, MMC 814, 420 Delaware St. SE, Minneapolis, MN, 55455
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
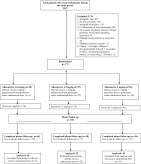
Fig. 1
Study Flow Diagram
Abstract
Objective
To compare need for re-dosing, sedation efficacy, duration and adverse events between three commonly administered doses of parenteral ketamine in the Emergency Department (ED).
Methods
We conducted a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial on a convenience sample of children 3–18 years who received IV ketamine for procedural sedation. Children from each age group (3–6,7-12,13-18 years) were assigned in equal numbers to 3 dosing groups (1, 1.5 and 2 mg/kg) using random permuted blocks. The primary outcome measure was need for ketamine re-dosing to ensure adequate sedation. Secondary outcome measures were sedation efficacy, sedation duration, and sedation related adverse events.
Results
171 children were enrolled of whom 125 (1mg/kg: 50,1.5 mg/kg :35, 2mg/kg: 40)received the randomized dose and were analyzed. The need for ketamine re-dosing was higher in the 1 mg/kg group (8/50; 16.0% vs. 1/35; 2.9% vs. 2/40; 5.0%).There was no significant difference in the median Ramsay sedation scores [5.5 (IQR:4,6) vs. 6 (IQR:4,6) vs. 6 (IQR:5,6)]; FACES-R score [0 (IQR:0,4) vs. 0 (IQR:0,0) vs. 0 (IQR:0,0)], sedation duration in minutes [23 (IQR: 19,38) vs. 24.5 (IQR: 17.5, 34.5) vs. 23 (IQR:19,29)] and adverse events (10.0% vs. 14.3% vs. 10.0%) between the 3 dosing groups. Physician satisfaction was lower in the 1mg/kg group (79.6% vs. 94.1% vs. 97.3%).
Conclusions
Adequate sedation was achieved with all three doses of ketamine. Higher doses did not increase the risk of adverse events or prolong sedation. Ketamine administered at 1.5 or 2.0 mg/kg IV required less re-dosing and resulted in greater physician satisfaction.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
An abstract of this study was presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting as a poster presentation , May 2013.
Grant Funding: This study was supported by the "New Investigator Grant Program", Children's Research Foundation Of Michigan as well as Children's Hospital of Michigan Foundation Grant.
Author Contributions: NK, MLL and MGR conceived the study and designed the trial. NK obtained research funding and supervised the conduct of the trial and data collection. MM performed the study randomization, study drug preparation, verification of the study drug dose administered. BW provided statistical advice on study design , analyzed the data and drafted the statistical analysis section of the manuscript. NK drafted the manuscript, and MLL and MGR contributed substantially to its revision. All authors have reviewed the manuscript. NK takes responsibility for the paper as a whole.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


